Sensirion, a leading manufacturer of various sensors, offers multiple types of sensors for measuring CO2 concentration – what are the differences between them, their advantages, and which sensor is best for battery operation? You will find out in this article.
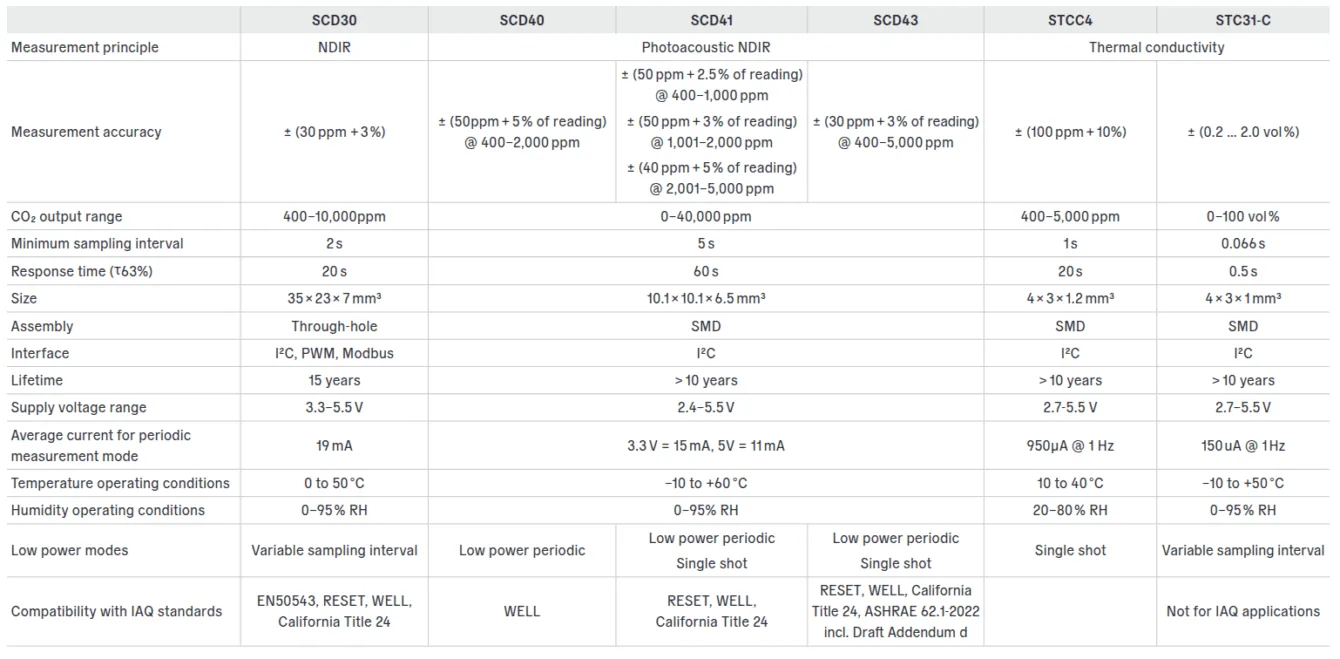
The SCD30, SCD40, and STCC4 sensors are all designed for measuring carbon dioxide (CO₂) concentration, but they use different technologies and differ in key parameters such as accuracy, power consumption, range, and measurement error.
1. Measurement Technology
SCD30: Utilizes NDIR (nondispersive infrared) technology with CMOSens® technology for CO₂ detection. It also integrates temperature and humidity sensors for measurement accuracy compensation.
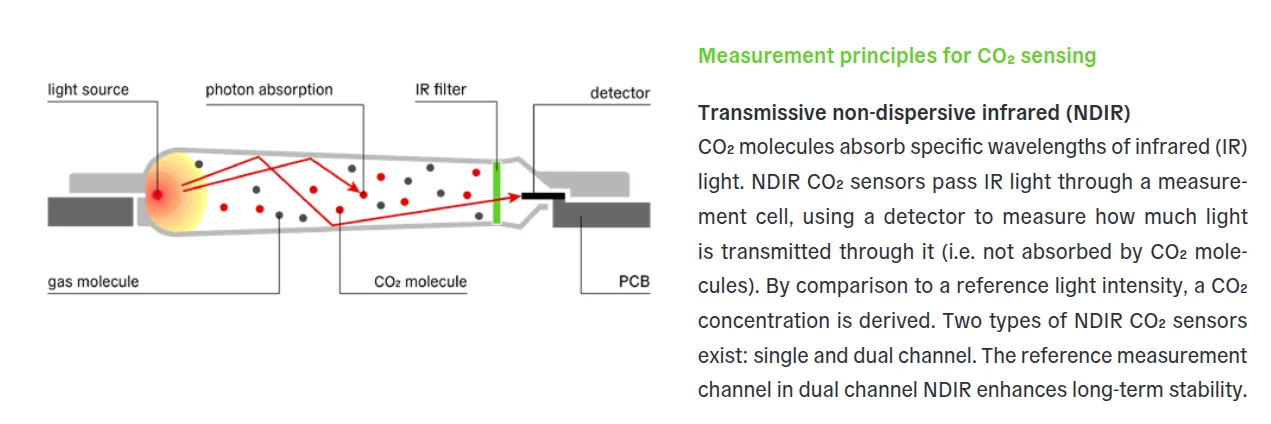
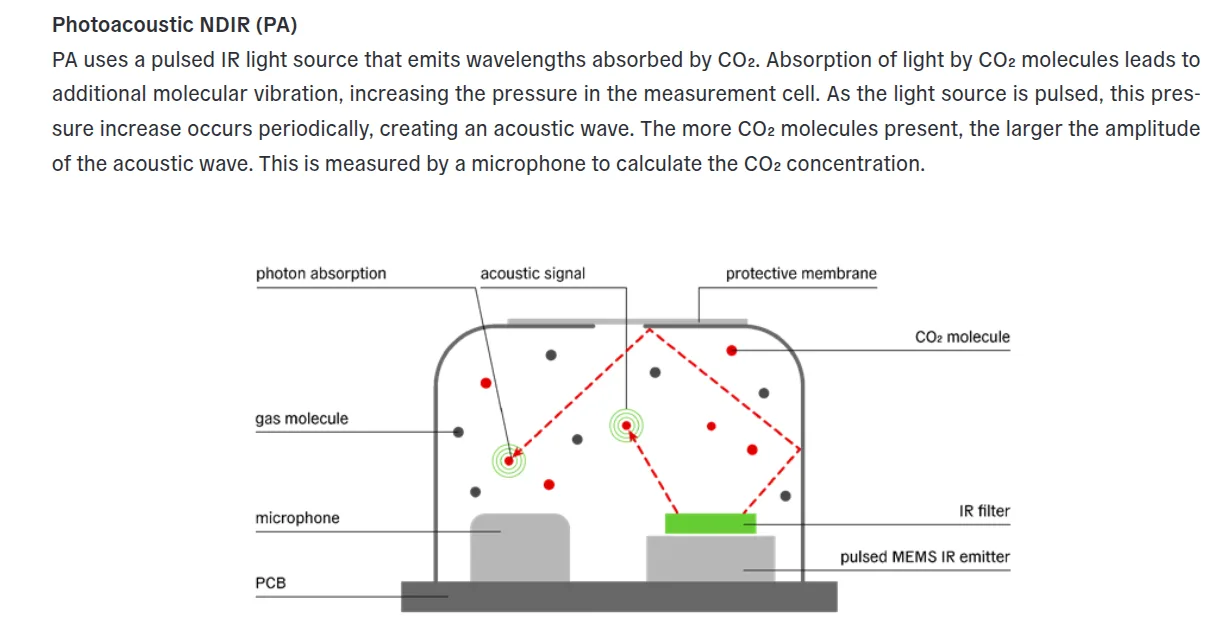
SCD40: Employs modern photoacoustic NDIR technology with patented PASens® and CMOSens® technology. It has an integrated chip for temperature and humidity compensation.
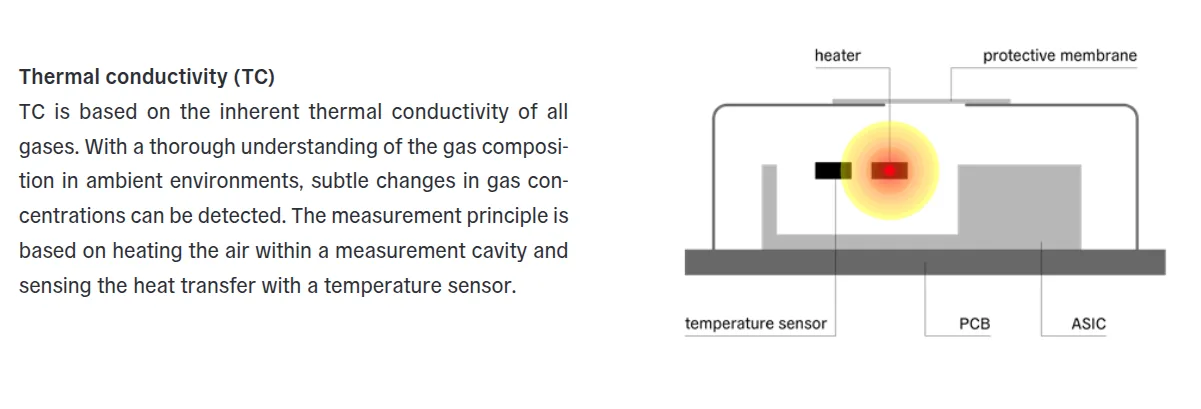
STCC4: Uses measurement based on thermal conductivity, which measures the different thermal conductivity of CO₂ compared to air. Humidity and temperature compensation is provided by an external SHT4x sensor.
2. Accuracy and Measurement Error
SCD30: Accuracy ±(30 ppm + 3% of the value) in the range of 400–10,000 ppm.
SCD4x: Accuracy ±(50 ppm + 5% of the value) in the range of 400–2000 ppm (SCD40). For SCD41, it is ±(40 ppm + 5% of the value) in the range of 400-5000 ppm.
STCC4: Accuracy ±(100 ppm + 10% of the value) in the range of 400–5000 ppm with temperature compensation from the SHT40 sensor.
3. Maximum Measurement Range (without guaranteed accuracy and reliability)
SCD30: Measures CO₂ in the range of 400 to 40,000 ppm (for communication via I2C, UART) or 400-5000 ppm for data transmission via PWM. The reliable range is 400 – 10,000 ppm.
SCD40: Range 0 to 40,000 ppm. The reliable range is 400 – 2000 ppm (SCD40) or 5000 ppm (SCD41).
STCC4: Range 380 to 32,000 ppm. The reliable range is 400 – 5000 ppm.
The range of 400 – 5000 ppm is ideal for measuring CO2 concentration in households, as exceeding 2000 ppm is not uncommon, for example, in winter and in unventilated or poorly ventilated apartments.
4. Power Consumption
SCD30: Current consumption of approximately 19 mA with one measurement every 2 seconds.
SCD40: Low consumption, less than 0.4 mA on average at 5 V with measurements every 5 minutes.
STCC4: Very low consumption, about 950 µA (0.95 mA) in continuous mode, around 100 µA for a single measurement (once every 10s). In sleep mode, it draws only 1 µA.
5. Supply Voltage
SCD30: Operating voltage from 3.3 V to 5.5 V.
SCD40: Wider supply voltage range from 2.4 V to 5.5 V.
STCC4: Supply voltage from 2.7 V to 5.5 V.
6. Additional Features
STCC4 includes an ADDR pin that can be connected to GND or supply voltage, depending on the connection, it has a different I2C address (ADDR to GND -> 0x64, ADDR to VCC -> 0x65).
All three sensors measure, in addition to CO2 concentration, also temperature and humidity. STCC4 measures temperature and humidity thanks to the connected external SHT40 sensor.
Note: if you are designing your own board with this sensor, the mounted SHT40 must have the address 0x44 (depends on the part number of the SHT40 sensor)
For the sensors, it is necessary to follow the design-in guide document, which informs how the sensor can be used, what situations to avoid, and where to appropriately place the sensor for the most accurate measurements.
SCD30 offers I2C, UART, or PWM as communication interfaces. SCD4x and STCC4 only support I2C.
The sensors include automatic calibration of the value when exposed to outdoor CO2 concentration (around 400 ppm) for a certain period.
7. Selection of Available Modules
Here is a selection of available modules; there are of course more manufacturers – Adafruit, Sparkfun, but they are less accessible in the Czech Republic.
SCD30

Available at mouser
price 668 CZK (excl. VAT, 19.8.2025)
SCD4x

Available at Laskakit
price 768 CZK (incl. VAT, 19.8.2025)

Available at mouser
price 795 CZK (excl. VAT, 19.8.2025)
STCC4

Available at mouser
price 1270 CZK (excl. VAT, 19.8.2025)
Conclusion:
SCD30 is suitable for applications requiring higher accuracy and a wider CO₂ measurement range with integrated humidity and temperature measurement, but with higher power consumption.
SCD40 offers a more compact solution with photoacoustic technology and very low consumption, but with a smaller range and slightly lower accuracy. A disadvantage is also the more demanding conditions for proper sensor placement due to the measurement technology used – drafts can easily disrupt measurements.
STCC4 is the most energy-efficient and smallest sensor based on thermal conductivity, but has the lowest accuracy and narrower range, suitable for demanding space- and energy-constrained applications.
Personally, I would consider using the STCC4 in a project, which is very small, energy-efficient, and suitable for battery operation when using sleep mode.
In terms of price, STCC4 also comes out as the cheapest option for measuring CO2 concentration.
For interest, I have included the STC31-C sensor in the table, which measures CO2 concentration as a percentage.
SCD30
datasheet https://sensirion.com/media/documents/4EAF6AF8/61652C3C/Sensirion_CO2_Sensors_SCD30_Datasheet.pdf
Product page https://sensirion.com/products/catalog/SCD30
Arduino library https://github.com/Sensirion/arduino-i2c-stcc4
SCD4x
datasheet https://sensirion.com/media/documents/E0F04247/631EF271/CD_DS_SCD40_SCD41_Datasheet_D1.pdf
Product page https://sensirion.com/products/catalog/SCD41
Arduino library https://github.com/Sensirion/arduino-i2c-scd4x
STCC4
datasheet https://sensirion.com/media/documents/6AED4B15/684A889C/CD_DS_STCC4_D1_3.pdf
Product page https://sensirion.com/products/catalog/STCC4
Arduino library https://github.com/Sensirion/arduino-i2c-scd30
CO2 measurement technology https://sensirion.com/media/documents/FBFDBE42/686D08CC/SE_Bro_CO2_Sensors_EN-web_250708.pdf